Information Utility & lodgment of Default under IBC, 2016
- Information Utility & lodgment of Default under IBC, 2016
- Information utility- “the warehouse of the financial information of debtor”
- National E-Governance Services Limited (NeSL)
- The obligation of an Information Utility
- Information of Default to be provided along with an Application made u/s 7 or Sec. 9 of the IB Code, 2016
- Procedure for submission of financial information to Information Utility
- Duties as an Interim Resolution Professional or Resolution Professional or Liquidator
- Directions of the Reserve Bank of India
- Final thoughts
- Download the copy:
Information Utility & lodgment of Default under IBC, 2016
Under the Insolvency & Bankruptcy Code, 2016 it is always very crucial for the Adjudicating Authority and the Insolvency Professionals to identify the reasonableness of default, dispute and other financial information of Debtors such as records of its debt, liabilities at the time of his solvency, assets over which the security interest is created by Debtor, timely records of its default and its financial statements of preceding years.
Once Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process gets initiated against any Corporate Debtor, the management of the affairs of such corporate debtor vest in the interim resolution professional and thereupon all the powers of the Board of Directors or the Designated Partners of the said Corporate Debtor shall stands suspended and the same is exercised by the interim resolution professional. During such phase it’s quite natural for any IP/ RP’s to face non-cooperation from the management and suspended Board of the Corporate Debtor in this regards for many of the financial information of the corporate debtor, the interim resolution professional/ resolution professional usually rely upon the electronic records of corporate debtor available with the Information utility.
Even at the admission stage of any application, it’s equally important for the Adjudicating Authority to avail and rely upon certain financial information pertains to the default committed by the Corporate Debtor and such information can only be considered reliable if the same is provided by or generated from some independent source.
Related Topic:
(VAT) GST Vs IBC : Tale of two judgments
Information utility- “the warehouse of the financial information of debtor”
In this connection, the concept of the Information utility (IU’s) has been brought by the Insolvency Code, who acts as a financial data repository or data warehouse by collecting, collating, authenticate, verify, store and disseminate financial information of debtors to facilitation swift decision making in the resolution proceedings. It provides an effective retrieval facility to the Insolvency Professionals, Debt Recovery Tribunal, and the National Company Law Tribunal to enable them to deals with the proceedings of Resolution Process or Liquidation in a time-bound manner.
The Information Utility collects, collate, authenticate and disseminates financial information. The purpose of such collection, collation, authentication, and dissemination of financial information of debtors is to facilitation swift decision making in the resolution proceedings.
National E-Governance Services Limited (NeSL)
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) has registered National EGovernance Services Limited more popularly known as NeSL as the first IU under the IBBI (IUs) Regulations, 2017 on September 25, 2017.
NeSL is owned and promoted by leading public institutions like State Bank of India, Life Insurance Corporation, Canara Bank, Bank of Baroda, ICICI Bank, CDSL, HDFC, Axis Bank, Union Bank of India and NABARD among others and is incorporated as a union government company.
Their role is to serve as an information repository of any debt or any claim of the Corporate Debtor submitted to it by the financial creditor or an operational creditor or by the Debtor itself through its authorized representative like Auditor or by Co-Applicant or Co-borrower, or Guarantor where the information is used to get verified and authenticated and disseminated for the purpose of adjudication.
The obligation of an Information Utility
There are several obligations on the part of the Information utility as broadly provided under Sec. 214 of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016, such as
a) To create and store financial information in a universally accessible format;
b) To accept electronic submissions of financial information from persons who are under obligation to submit financial information under sub-section (1) of section 215.
c) To accept the electronic submissions of financial information from persons who intend to submit such information;
d) To get the information received from various persons authenticated by all concerned parties before storing such information;
e) To provide access to the financial information stored by it to any person who intends to access such information
f) To publish such statistical information and to have interoperability with other information utilities.
Information of Default to be provided along with an Application made u/s 7 or Sec. 9 of the IB Code, 2016
Section 3(12) has defined the default which means non-payment of debt when whole or any part or installment of the amount of debt has become due and payable and is not paid by the debtor or the corporate debtor, as the case may be.
The provision of the Code requires an applicant Financial Creditor under subsection (3) of Sec. 7 of the IBC, 2016 to furnish along with an application the record of the default recorded with the information utility and the Adjudicating Authority on receipt of an application ascertain the existence of a default from the records of an Information Utility.
Also, Rule 5(3) of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy (Application to Adjudicating Authority) Rules, 2016, requires an Operational Creditor to file with the Information Utility the details with regards to the service of Demand notice or Invoice demanding Payment to the Corporate Debtor.
Along with Form No. 3 i.e. Form for Demand Notice, the operational creditor may also attach a certificate from an information utility confirming that there is no record of any dispute filed by any person at any point of time with the information utility in relation to the relevant operational debt for which the Demand Notice is served to the Corporate Debtor. Meaning thereby even the Corporate debtor should also promptly opt for lodging any dispute with regards to any of its operational debt if there is the existence of any dispute with regards to the amount of debt or the quality of goods or service or any breach of a representation or warranty irrespective of the fact that whether any suit or arbitration proceedings relating to the same is pending or not.
Also u/s 9 of the Code, the operational creditor may also provide the record with information utility confirming that there is no payment of an unpaid operational debt by the corporate debtor.
Meaning thereby such Certificate & data furnished by the Information utility are considered and accepted by NCLT/DRTs as legal evidence.
Procedure for submission of financial information to Information Utility
An information utility shall accept the information submitted by a user in Form C as provided in Schedule forming a part of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (Information Utilities) Regulations, 2017). Meaning thereby before submitting any financial information, the person has to enroll itself as a “User” with Information Utility by declaring its identity and furnishing certain documents such as Aadhaar, PAN, CIN Number, etc. The Information utility thereafter verifies the identity of the person and only on successful verification the User Registration shall be considered successfully completed and the User Id shall be communicated to the person through an e-mail.
On receipt of the information, the information utility shall assign a unique identifier to the information and notify the user with regards to the unique identifier of the information, the terms and conditions of its authentication, its verification and the manner in which the information may be accessed by other parties.
An information utility expeditiously undertakes the process of authentication and verification of information of default as soon as it is received. The information utility shall deliver the information of default to the debtor concerned seeking its confirmation. Information Utility shall send reminders to the debtor at least 3 times for confirmation of information of default and in case, if the debtor does not respond, shall allow three days each time for the debtor to respond and on completion of the process the information utility shall record the status of authentication of information of default in a manner provided as under:
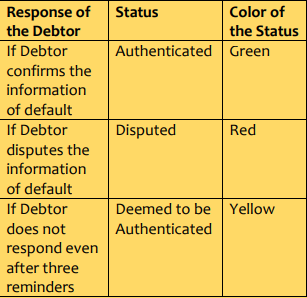
After recording the status of information of default, the information utility shall communicate the status of authentication in physical or electronic form of the relevant color, as indicated above, to the registered users who may be either the (a) Creditors of the debtor who has defaulted or the (b) Parties and sureties, if any, to the debt in respect of which the information of default has been received.
Duties as an Interim Resolution Professional or Resolution Professional or Liquidator
It is the duty of an insolvency professional to submit financial information, reports, registers and minutes in respect of any insolvency resolution, liquidation or bankruptcy proceedings to an information utility for storage and the information utility shall not provide any access to such information, reports, registers and minutes to any person other than the concerned insolvency professional, the Insolvency Board, and the Adjudicating Authority.
Directions of the Reserve Bank of India
The Reserve Bank of India vide its order dated December 19, 2017, has directed all financial creditors regulated by it such as has directed All Scheduled Commercial Banks, Small Finance Banks, Local Area Banks, All Co-operative Banks, All NBFCs and All India Financial Institutions to adhere to the relevant provisions of IBC, 2016 and IBBI (IUs) Regulations, 2017 and immediately put in place appropriate systems and procedures to ensure compliance to the provisions of the Code and Regulations.
Final thoughts
One of the key aspects of the IBC, 2016 is its timeliness of Resolution or Liquidation or Bankruptcy Process and in order to timely complete the process the authenticity of financial information plays a very significant role.
The information on which the confidence can be easily reposed by the resolution professional or liquidator or a bankruptcy trustee or an adjudicator and on the basis of which the adjudication process can smoothly take place and in this regards the role of Information Utility is noteworthy and significant in this Code.
Download the copy:
If you already have a premium membership, Sign In.
 PCS Vinit Nagar
PCS Vinit Nagar
Mr. Vinit Nagar is a Practicing Company Secretary and having an overall post qualification experience of about 9 years. He is founder of M/s Vinit Nagar & Co. Company Secretaries. His Core areas of Practice includes Corporate Restructuring and appearances before National Company Law Tribunal, Region Directors, Registrar of Companies, SEBI and Securities Appellate Tribunal. His expertise in area of Practice is advisory under the Corporate Law Compliances & Drafting and Appearance in Litigation and Non Litigation matters.