FAQs on Income under head House Property – all you need to know.
- What is income from House Property?
- How many house properties can be self occupied by an assessee?
- What are the deductions for calculation of Income from House Property?
- How to calculate Gross Annual Value of House Property?
- How to calculate income of Self Occupied house property?
- How to calculate Income from Let Out house property?
- What is the limit of interest on a housing loan?
- What are tax benefits on Home Loan?
- What are the set off provisions of loss from house property?
- What are carry forward provisions of loss from house property?
- Comparison:
What is income from House Property?
The total income is divided into five heads for taxability.
- Income from Salary
- Income from house property
- Income from business & profession
- Income from Capital gains
- Income from other source
Out of these heads income from house property is taxed in the second head. Any income arising due to let out of a house property is covered in this head. But any income on sale of a house property is covered in Capital gains and not in Income from house property. Also any income from a commercial property is also not covered in this head.
How many house properties can be self occupied by an assessee?
Prior to Budget 2019, when an assessee owned more than one residential houses, only one was considered to be self occupied and the rest were considered to be deemed let out. But after Budget 2019, an assessee is allowed to own two houses as self occupied houses and more than two houses will be considered as deemed let out.
So for example, Mr A owns three residential houses in FY 2020-21 then, in such a case two houses will be deemed as self occupied and one will be deemed let out.
What are the deductions for calculation of Income from House Property?
Section 24 of Income Tax Act provides three types of deductions under Income from House Property. These are:
Standard Deduction
Assessee can claim 30% of the Net Annual Value as a deduction of repairs, rents and so on (irrespective of the Actual expenditure incurred). If the Gross Annual Value is nil this deduction is not applicable
Home Loan Interest
Assessee can claim deductions for interest on home loans taken for the purchase, construction, reconstruction and repair under this section.
Municipal Taxes
While calculating income from house property, a taxpayer is allowed deduction of municipal taxes paid in respect of the house property only if it is let out or deemed to be let out. In case of a self occupied house property, the annual value of the property shall be nil and thus, deduction of municipal taxes shall not be possible.
How to calculate Gross Annual Value of House Property?
In case of Self Occupied House Property:
The annual value of self occupied property is always nil. Where a person has more than one self occupied property then value of self occupied property can be specified as nil. Properties other than the self occupied may be let out or vacant. If they are let out the rent income is taxable. If they are vacant, still they are deemed as let out for taxation purposes. In this case their expected rent is taxable.
In case of Let Out of House Property:
The annual value of Let Out House property is Higher of A or B in the following diagram:
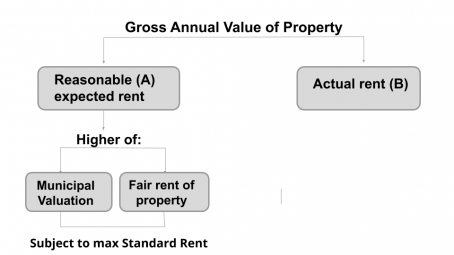
Note: Reasonable Expected Rent is the amount for which property can be expected to be let out from year to year.
How to calculate income of Self Occupied house property?
In order to understand the calculation of income from self occupied house property let’s take an example:
Miss Girdharwal owns a house property, municipal value of which is Rs 2,75,000 and municipal taxes paid by her is Rs 50,000. Interest on home loan paid by Miss Girdharwal is Rs 3,00,000. Compute her income.
|
Particulars |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
A.Gross Annual Value (for self occupied properties, GAV is considered NIL) |
NIL |
|
B.Less: Municipal Taxes (For self occupied, municipal taxes are considered) |
NIL |
|
Net Annual Value (A-B) |
NIL |
|
Less : Interest on home loan As per section 24,(interest is restricted to Rs 2 lakh) |
(2,00,000) |
|
Income from House Property |
(2,00,000) |
How to calculate Income from Let Out house property?
As discussed above, assessee owning more than two houses for FY 2019-20, any house more than two houses shall be considered as deemed let out properties. Lets understand with the help of an example :
Mr. A owns a house property which is let out throughout the year. Municipal Value is Rs 1,45,000, Fair rent Rs 1,36,000, standard rent Rs 1,24,000 and actual rent received Rs 1,15,000.Municipal taxes paid by the tenant Rs 5,400. Interest on home loan paid Rs 3,50,000. Apart from this, he also has income from Business of Rs 6,50,000.
Compute net income of Mr A from house property
|
Particulars |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
A.Gross Annual Value Reasonable Rent: (A) 1,24,000 Higher of MV and FR 1,45,000 Maximum to Standard rent i.e. 1,24,000 Actual rent received: (B) 1,15,000 GAV is higher of A and B |
1,24,000 |
|
B.Less: Municipal Taxes (In case of deemed let out, municipal taxes can only be claimed if paid by the owner and here, tenant has paid) |
NIL |
|
Net Annual Value (A-B) |
1,24,000 |
|
Less : Interest on home loan |
(3,50,000) |
|
Income from House property |
(2,26,000) |
|
Less: Set off from Business income (restricted upto Rs 2,00,000) |
2,00,000 |
|
Net Income From House property |
(26,000) |
What is the limit of interest on a housing loan?
Under Section 24, the limit for interest deduction for a self occupied property is Rs 2 lakh whereas for let out property, there is no limit defined under this section. However, if a loan is taken for repair or renovation of the self occupied property, the limit is Rs 30,000.
What are tax benefits on Home Loan?
- Tax deduction on home loan interest u/s 24: Section 24 prescribes deduction of interest paid on home loan but restricted upto Rs 2 lakhs for self occupied properties where interest is further categorized into pre construction period and post construction period.
- Tax deduction on principal repayment: Section 80C provides deduction on principal repayment of home loan upto Rs 1.5 lakhs in one FY.
- Additional tax deduction u/s 80EEA: This section was inserted in Budget 2019 to provide additional tax benefits to home buyers having 5 house property upto Rs 45 lakhs on the interest on home loan upto Rs 1.5 lakhs. This deduction is over and above deduction u/s 24.
What are the set off provisions of loss from house property?
Intra Head Adjustment
It means setting off losses under the same head to which they belong. Any loss that occurs under head house property, such loss is allowed to be set off against income under head house property.
Inter Head Adjustment
Here inter head adjustment means loss under one head of income can be set off against income from another head of income but in the same previous year (for carry forward of losses Inter head adjustment is not allowed).
Therefore, any loss under head house property is allowed to be set off against income under any other head subject to the maximum limit of Rs 2,00,000.
What are carry forward provisions of loss from house property?
Loss from house property which cannot be set off in the same assessment year is allowed to be carried forward for 8 years. Reasons for loss from house property could not be set off in the same assessment year are:
- Absence/inadequate of income under the other head.
- Loss under head house property exceeds limit of Rs 2 lakhs in PY.
Comparison:
|
Type of house property |
Self occupied |
Let out |
|
Gross annual value |
Nil |
xxx |
|
Less: Municipal taxes |
Not applicable |
xxx |
|
Net annual value |
Nil |
xxx |
|
Less: deduction u/s 24:
|
Not applicable Limit to Rs 2 lakh p.a |
30% of NAV No limit |
|
Income from house property |
xxx |
xxx |
If you already have a premium membership, Sign In.